Abstract
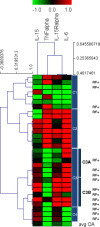
Results 432 patients were screened: 107 were randomised to tumour necrosis factor inhibitors and 101 started taking; 107 were randomised to the combined drug strategy and 104 started taking the drugs. Initial assessments were similar; 16 patients were lost to follow-up (seven with the tumour necrosis factor inhibitor strategy, nine with the combined drug strategy); 42 discontinued the intervention but were followed-up (19 and 23, respectively). The primary outcome showed mean falls in scores on the health assessment questionnaire of −0.30 with the tumour necrosis factor inhibitor strategy and −0.45 with the alternative combined drug strategy. The difference between groups in unadjusted linear regression analysis favoured the alternative strategy of combined drugs. The mean difference was −0.14, and the 95% confidence interval (−0.29 to 0.01) was below the prespecified non-inferiority boundary of 0.22. Improvements at 12 months in secondary outcomes, including quality of life and erosive progression, were similar with both strategies. Initial reductions in disease activity were greater with the biologic strategy, but these differences did not persist beyond six months. Remission was seen in 72 patients (44 with biologic strategy; 36 with alternative strategy); 28 patients had serious adverse events (18 and 10, respectively); six and 10 patients, respectively, stopped treatment because of toxicity. The alternative strategy reduced health and social care costs per patient by £3615 (€4930, $5585) for months 0-6 and £1930 for months 6-12.
Conclusions In patients with active rheumatoid arthritis who meet English criteria for biologics an alternative strategy with combinations of intensive synthetic disease modifying drugs gives non-inferior outcomes to treatment with tumour necrosis factor inhibitors. Costs are reduced substantially.
Via Krishan Maggon



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...







BMJ 2015; 350 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.h1046 (Published 13 March 2015)Cite this as: BMJ 2015;350:h1046